In life, we’re constantly comparing one thing to another.
You could say we have a critical eye. But it could also be said that we have an eye for quality. For example, apples and oranges are comparable.
They may fit into the same fruit category, but they will appeal to different people based on their individual needs.
If you’re looking for a Vitamin C hit, you’ll probably want an orange on your plate. However, if you’d like more fiber in your diet, you’ll probably bite into a juicy apple. It doesn’t necessarily mean one is better than the other – it comes down to preference.
And the same thing can be said about SVG vs PNG formats.
In this article, we will be comparing the two formats when it comes to web and digital design.
Jumpstart your ideas with Linearity Curve
Take your designs to the next level.
Important differences between SVG and PNG
What’s an SVG?

SVG is an image file format created specifically for designing two-dimensional vector and vector-raster graphics for websites. SVG supports animation, transparency, gradients, and is easily scalable without losing quality.
SVG is also the most widely used vector file format on the web.
It’s important to note that in Linearity Curve, you can export your document to a vector (SVG) format.
Let’s break this down:
- Scalable: SVGs can be resized up without damaging the quality of the image. It will be perfectly crisp and clear, no matter how large it is.
- Vector: Most image file types contain pixels. Vectors are essentially pieces of code that render an image in real-time, converting it to the pixels you see on your screen. While they display the same image, what goes on in the background is very different.
- Graphics: Though it may not be as well known, SVG is an image file type like PNG, JPEG, or GIF. It just goes about things a little differently.
Vectors are pieces of code written in XML that represent shapes, lines, and colors to elaborate on how it works. While creating an image with nothing but code is entirely possible, most people use a vector graphics editor.
You can also convert PNGs or other raster format images to SVG, but the results aren’t always great.
SVG also supports animation and transparency, making it a versatile file format. The only issue is that it’s not as widely used as more standard formats like PNG, so it’s less supported on older browsers and devices.
It’s also not always the easiest to upload it to your site and get it to display correctly.
Pros and cons of SVG

Here’s why people enjoy SVGs:
- SVGs always look high quality due to never experiencing high definition loss. A raster image format can start to look blurry when even slightly resized.
- As SVGs are just CSS code, their file size is minimal and well-optimized. SVG optimization also exists to make them even more manageable. Your site will also likely load a little faster if you use them instead.
- Using traditional PNGs means that images have to be referenced as external resources. All those PNGs mean an increase in ‘http’ requests and, thus, a slower site. SVGs are not only smaller in file size, but the XML can be embedded inline to your HTML, eliminating ‘http’ requests.
- SVGs can be animated and styled with CSS code. This includes changing the colors. Animations, for example, such as transformations and transitions, that you use on HTML elements can also be used on an SVG element. There are however instances where you can’t use CSS to animate SVGs, but these instances can usually be covered with JavaScript.
- There are many ways SVGs can be used on the web, such as displaying logos. Logos are usually vector based, and rightly so. The beauty is that you could define an SVG document as your logo and then use it wherever you like without worrying about size, resolution, or load times.
- Google indexes SVGs, which is good news. SVG content, whether in a standalone file or embedded directly in HTML, is indexed.
SVG has quite a bit on PNG, from being scalable to tinier in size, but it’s not better in every situation. Let’s have a look at the downside of vector file types:
- As mentioned earlier, while SVGs enjoy support on all major modern browsers, you can run into compatibility issues rendering them on older browsers and devices. If a significant chunk of your visitors uses those, switching over could be a bad idea.
- SVGs are harder to work with, requiring special programs to create and edit. While you can design them with nothing but XML, this isn’t always feasible.
- SVGs aren’t nearly as easy to embed as PNGs. If you’re using WordPress, it isn’t supported by the default media library, so you’d need a plugin to upload them. This can become more costly in the long run. SVGs must be rendered by the browser when the page is loaded, so using excess or a large file with many vectors can burden the device.
When to use SVG over PNG
SVG is not intended for social media. Instead, SVG works best for web design when you’re exporting icons and illustrations for websites with responsive design and objects that should be displayed perfectly on screens.
Use SVG when you want transparent images that can be easily zoomed or compressed, need lightweight animations, or plan to modify an image soon or frequently.
While you definitely shouldn’t convert all your PNGs to SVGs, vector graphics can make an excellent replacement for some images. SVG images also work exceptionally for decorative website graphics, logos, icons, graphs and diagrams, and other simple images.
However, they don’t work as well with complex images involving many colors and shapes, such as screenshots, photography, and detailed artwork.
While it’s possible to convert any image to SVG, browsers don’t always handle complex vectors with hundreds of colors well since they must be rendered when the page loads.
Ready to learn something new?
Check out our list of great design courses online.
In addition, SVG artwork can be beautiful, but designing complex images requires a lot of time, effort, and proficiency in advanced editing tools. Keep it simple if you want to create your vector images. If you have detailed images, definitely stick with PNG.
However, SVGs are better for responsive and retina-ready web design due to their scalability and lack of quality degradation. In addition, they support animation while PNG doesn’t, and raster file types that support animation like GIF and PNG.
In a nutshell, for simple graphics that may require animation and are guaranteed to scale well on any screen size, use SVG.
What is a PNG?

PNG stands for Portable Network Graphics, and this name is reflected in how widespread this file type is. Anyone who’s ever used a computer has likely worked with PNGs, as it’s the most common file type on the internet next to JPEG.
PNG is a raster image file type, similar to most common image formats. That means it consists of pixels, the same small dots displayed on your monitor or screen.
While this makes it easy to display, it also means image quality is dependent on the resolution – how many pixels are in the image.
So, if you enlarge a raster, the quality will be impacted. Sometimes, the damage is negligible, especially when scaling up, and sometimes it can make an image blurry and completely unusable.
This is because when you stretch it, you lose the visual quality. This is why you must not upscale a PNG beyond its intended resolution.
Still, the prevalence of PNG makes it a good candidate for general-purpose usage. This file type supports transparency but not animation.
Pros and cons of PNG

What makes PNG the most widely used image file format online?
- Whether you’re coding from scratch or using the WordPress media manager, displaying PNG images on your site is a simple task.
- PNG uses lossless compression that leaves it looking crisper than glossy compression JPEGs. However, this comes at a larger file size cost and can’t compare to vector images. PNG uses better image compression technology than GIF, allowing for smaller files that download more quickly.
- With higher bit depths (more colors), PNG allows for 1, 2, 4, 8, 16, 24, and 32-bit images, smashing the 8-bit barrier.
- Multiple layers of transparent PNG images allow for full alpha channel transparency, which makes moving images from one background to another easy.
- Built-in gamma correction allows users to see an image the way it was intended to be seen by selecting the gamma level intended for their monitor.
On the other hand, the PNG format was created decades ago and has several notable flaws that haven’t been updated for the modern era:
- You need to plan when designing raster graphics and ensure it’s the right size, or you may waste time making unusable images.
- PNGs are very large due to their lossless compression. Thus, they can slow down your website. Fixing this requires compressing it even more, which can damage the quality.
- Making images ‘retina-ready’ is more tedious with PNGs and more likely to cause blurriness.
- PNG does not support animation. Other animated raster file types like GIFs can have serious problems. For instance, GIFs are super low quality and only support 256 colors.
When to use PNG over SVG

If you're using high-quality images, detailed icons, or need to preserve transparency, SVG is the best choice. Use it for small static images, logos, navigation elements, prints, and other images with transparent backgrounds and robust edges.
When you’re not sure whether a platform will handle the newer, less supported SVG file type, PNG is the way to go. For instance, you can’t upload SVGs to most social media sites as they aren’t supported file types.
And as some email templates may struggle with vectors, it’s usually recommended to stick with PNGs.
In general, PNGs work well with complex, non-animated images, especially ones that require transparency. You can use it pretty much anywhere – it’s just that sometimes an SVG would be a better fit.
Remember that you can always use PNG fallbacks if your SVG fails to load, so it’s usually safe to go with vectors, even if a significant portion of your user base has stuck with older devices or browsers.
How to create an SVG file
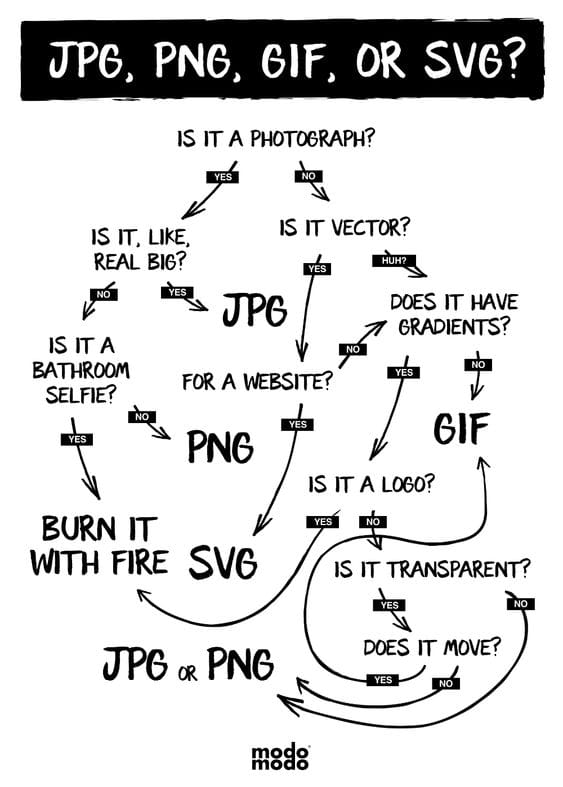
To create an SVG file, you need to have a vector version of the logo or illustration. Vector art is defined in terms of 2D points connected by lines and curves to form polygons and other shapes with different properties.
A vector graphic is generated by creating nodes and joining these together with lines (known as paths) to build shapes. Moreover, vector art is used for multiple types of design projects. It's used for graphic design, illustration, and digital arts.
Vector software can be used for most forms of graphic design. It’s up to you, as the designer, to decide which type of software is most appropriate for your particular design project.
We happen to know a great vector software. Maybe you’ve heard of it? Linearity Curve is a design software that is free to use and perfect for creating vector graphics.
Ready to create brand assets that pack a punch?
Visit our Academy for free marketing design courses.
These are some of the main areas that use vector art and graphics to create high-quality, imaginative, scalable images:
- Illustration has become a very in-demand profession, with brands going crazy for authentic visual content to capture their persona and products beautifully.
- Vector art is used for many elements that go into the design of a website, including icons, logos, illustrations, and layout.
- You'll need vectored images to print posters successfully. Poster design can be used for art and decor, film, and marketing. Need poster design inspiration? Check out these scary movie posters that are sure to keep you awake at night.
- Most graphic designers use vector software to create logos. Why? Because vector graphics are easily scalable, simple to edit, and have tons of exporting options.
- Like posters and logos, vector designs are perfect for billboards as these are printed at an enormous scale. Your vector files will be necessary to maintain the quality of the image.
- Video game designers use all kinds of software. It is a highly complex form of design. The critical component of the artwork is generated using vector art. This type of vector art is especially popular lately with the growing popularity of video games and virtual reality.
It's a good idea to find out more about how to draw and work with vector art. You can also watch this tutorial video we made on how to easily create your own vectors using our top-notch software.
How to create a transparent PNG background file
A transparent background for your PNG may seem like such a basic design element. But, more often than not, these simple design techniques turn out to be some of the most valuable and creative ways to make your image stand out.
Here are some design tips on using a transparent background in your PNG to your advantage:
- Using a transparent background might not be the most common way to focus on a specific area you want to emphasize. Nevertheless, if you use it correctly, a transparent PNG background will help you put any part of your image into the spotlight. You can also use this technique to guide the viewer and give the whole design more perspective.
- Readability is one of the essential parts of your design, primarily if you work in marketing or PR. If you need to include the brand’s name and a one-liner, the design you want to use might not be the best to add text on top of it as it can be hard to read the letters.
- Want to create a multi-dimensional image? Then adding layers on top of layers will help you with that. Using a transparent background, in this case, is also going to help you add more depth. This technique is not very often used, so we recommend you use it only when you need to and when it makes sense considering the intention of your design.
- You can export your company logo in PNG with a transparent background for various applications without an obstructive white or black background, giving it a cleaner look.
If you’d like to get a step-by-step guide on how to achieve the above tips, you can check out our simple guide here.
Wrapping up

SVG and PNG are two very different file formats, which is why picking between them is an important choice.
You’re far more likely to use PNGs as it’s a simpler, easier-to-access, and more versatile file format. Complex images, such as screenshots and detailed illustrations, should use PNG.
Whenever it’s appropriate to use vector images – such as decorative graphics and logos – definitely use SVG. This is because they are responsive and have smaller file sizes. Just remember that SVGs can only be used or stored as vectors.
So, are you team SVG or PNG? We’d love to hear from you to find out!
Jumpstart
your ideas with
Linearity Curve
Take your designs to the next level.

:quality(75))
:quality(75))

:quality(75))
:quality(75))
:quality(75))